PacketStream started its journey in California in 2018, when it was established by the entrepreneur duo Arthur Aivazian and Ronald Bell. They imagined it as a company solving a particular need in the market - offering a network of peer-to-peer (P2P) residential proxies, which are IP addresses sourced from real devices around the world, allowing users to bypass geographic restrictions when accessing various kinds of data.
As opposed to many other residential proxy providers, which are centralized, PacketStream’s peer-to-peer nature allows acquiring and selling residential proxies to customers directly. In other words, users buy or sell residential IPs from and to one another. This system makes proxies cheaper, albeit at the cost of reliability and speed.
Another problem that this platform could face is the risk of unreliable IP addresses potentially being added to the network. This is because PacketStream, despite offering secure proxies in general, doesn’t entirely control the IPs sold through its network.
PacketStream: Plans and Pricing
Unlike many proxy providers out there with complex pricing plans, PacketStream keeps things simple, charging per bandwidth, with a flat fee of $1 per GB. This way, you get access to the entire network of residential proxies, which is a lot more straightforward and may even be a cheaper alternative to providers charging for individual IP addresses.
Indeed, $1 per GB is one of the most affordable pricing options in the industry, as most competitors charge a lot more. These include IPRoyal with $6.5 per GB, Bright Data with $8.40 per GB, and Webshare with $2.8 per GB (depending on the specific package you selected).
That said, you’ll need to purchase at least 50 GB, which will set you back by $50. This means you can’t buy just $1 of bandwidth to take the platform for a spin before deciding - the 50 GB minimum is a must. Still, PacketStream offers rotating proxies (alongside their static counterparts), so if one IP address doesn’t work, you can switch to a different one in a jiffy.
PacketStream offers a free trial, but without a standardized process. You need to contact the sales team to request this trial, which is futile for most individual users. The free trial is only suitable for people who plan to spend significant sums on proxies. After all, why contact a sales team if you just need to test a few gigabytes worth of proxies?
PacketStream accepts payments through PayPal and major credit cards.
PacketStream: Features
PacketStream allows users not just to buy proxies, but also to acquire them and sell them on to offset costs, and sell your unused device bandwidth for profit, offering it at prices starting at $0.10 per GB. The minimum payout is $5 and is sent to your PayPal account once per week with a 3% fee applied to cashouts.
Interestingly, Microsoft Defender blocked the download and installation of PacketStream, identifying it as a program that “displays deceptive product messages.” This is typically how ‘scareware’ is described, or software that makes deceptive or fraudulent claims about your computer’s health to trick you into buying unnecessary or potentially unwanted products, which may not be inherently malicious in the same way as other malware.
However, since PacketStream doesn’t make any scary claims about your device, the flagging as potentially malicious could be due to the application’s process of using your computer to route third-party traffic when you share your bandwidth with other users. Hence, the antivirus interprets the app’s behavior as unusual or questionable. So, if you fail to install PacketStream, this could be the reason.
Residential Proxies
PacketStream offers a P2P residential proxy network spanning 190 countries. These proxies are sourced from real devices whose owners sell their bandwidth on the PacketStream network. You don’t have to worry about illegally sourced IP addresses, a major problem plaguing proxy providers. Every IP address on PacketStream was consensually added by its owner to earn money.
The company has both randomized and static IP options on offer, with randomized IPs changing with every new request to provide a high level of anonymity. Static IPs, on the other hand, remain consistent for scenarios where a single and steady IP address is required. Selection of the type of residential proxy you need is done as part of the request when buying access.
PacketStream’s proxy IP addresses were reliable during our test and offered reasonable speeds. We chose IP addresses from different countries, and they provided fast connections, although the speed varies depending on the country. PacketStream lets you choose proxies from roughly 190 countries, but you can’t select by city, which we consider a disadvantage. Many rival proxy providers let you choose proxies from specific cities to increase your chances of evading geographical restrictions.
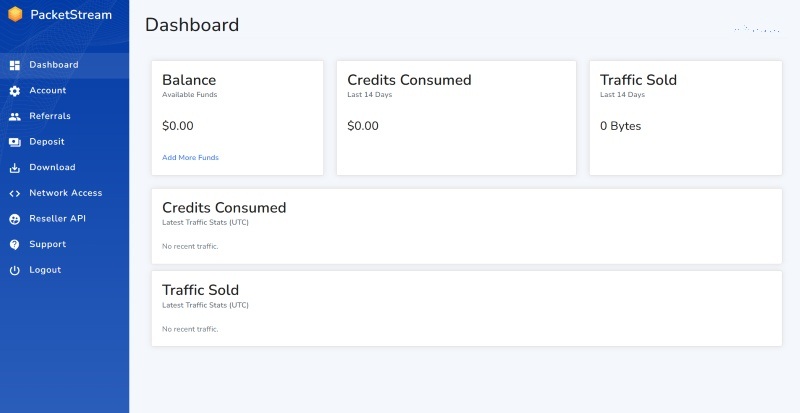
The platform supports HTTP, HTTPS, and SOCKS proxy protocols, which differ in how they handle traffic and their compatibility, each having its own strengths and downsides. Having the latter option in particular is important as it reduces network delays and provides better speeds than HTTP/HTTPS, making it ideal for high-speed, general-purpose tasks like P2P sharing or streaming. The other two, on their part, offer benefits like content caching and content filtering.
Residential proxies can be used for many things. A good example is data scraping, wherein people use proxies to bypass website geo-restrictions and scrape relevant information.
Suppose you run a website that tracks the prices of commodities and delivers this data to users. Running a price monitoring site requires extracting data frequently and quickly from many websites. The websites (primary data sources) are privy to external data scraping and block it by implementing geographical and IP restrictions. They can identify specific IPs from data scraping bots and block them from further access. They can also ban IP addresses of an entire country from accessing their information.
PacketStream gives you access to a large network of residential IP addresses to bypass restrictions and scrape commodity price data. If one IP address gets discovered and blocked, just switch to another and try your luck.) Although specific numbers may differ, this proxy provider has millions of IP addresses across 190 countries, so you’ll have no fear of running out of new proxies to bypass geographical restrictions on websites and services.
Online retail is another common use case for residential proxies. Many people use automated bots to snap up fast-selling products, placing orders before they run out of stock. However, e-commerce sites don’t like this and often blocklist bot IP addresses. PacketStream’s residential proxies let users circumvent this block and get their desired product.
As far as an e-commerce site is concerned, residential proxies belong to legitimate devices. It’s challenging for them to detect and block these proxies. Even when they do, you can switch to another proxy and visit the e-commerce site. PacketStream’s large network of residential proxies allows people to utilize automated scripts to bid for products.
One major drawback is that PacketStream offers only residential IPs. It doesn’t provide datacenter IPs, which are faster and more reliable. Datacenter IPs are sourced from dedicated servers with more speed, making them ideal for massive data scraping tasks. Large enterprises are the main users of datacenter proxies, but PacketStream doesn’t serve this cohort well. This proxy provider best suits individuals and small businesses seeking affordable residential proxies.
PacketStream doesn’t offer mobile-specific IPs. Mobile device IP addresses are present on this P2P network, but you can’t specifically choose that option. Many businesses use mobile IPs for app testing and ad verification, but performing these tasks with PacketStream is difficult.
Likewise, PacketStream doesn’t offer proxies sourced directly from Internet Service Providers (ISPs). ISP proxies provide higher data throughput and reduced delay than residential proxies, but you can’t get them on PacketStream.)
Selling Bandwidth
(PacketStream lets users sell their unused bandwidth and make money. You can add your IP address to the network and earn money when people use your device as a proxy. Pricing is $0.10 per GB, which can help you offset the cost of buying bandwidth on PacketStream.
Sharing your bandwidth requires downloading the PacketStream client on your PC. This client is available on Windows and macOS, as well as on Linux, where it can be installed by running a specific command via Docker. It can run even on low-end PCs. The primary requirement is a stable internet connection.
After installing the PacketStream PC app, you can open it anytime and activate a shared connection. Your payout is automatically calculated based on the amount of data your shared connection transmits. Closing the PacketStream app immediately terminates the shared connection, giving you complete control over the process. PacketStream can’t use your connection without your consent, which you give by opening the app.
There’s no limit to the amount of bandwidth you can share. The minimum payout is $5 for 50 GB of bandwidth, which makes sense because 50 GB is the minimum amount of bandwidth that PacketStream users can buy. A 3% fee applies to every payout.
Reseller API
PacketStream offers reselling/white-label services. This feature is for people interested in starting their own proxy providers. In that case, you can sell PacketStream’s proxies under your own branding and earn money. PacketStream provides a bare-bones version of its platform, which you can customize to build a brand atop the company’s infrastructure.
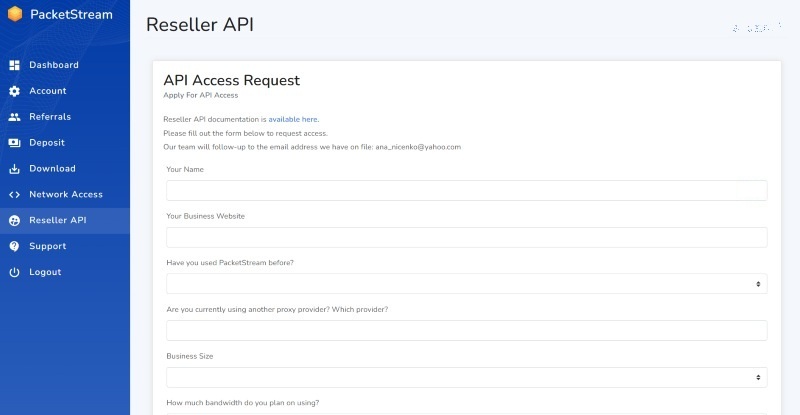
Resellers provide access to the same network of proxies available on PacketStream. Any device added to PacketStream’s network will become available on your proxy provider. This feature isn’t for individual users, but we consider it worth discussing to give a complete PacketStream review.
PacketStream: Ease of Use
PacketStream outshines many competitors in the user-friendliness criterion. It arguably has the simplest interface we’ve encountered in a proxy provider, thanks partly to its limited features (there’s not much to navigate).
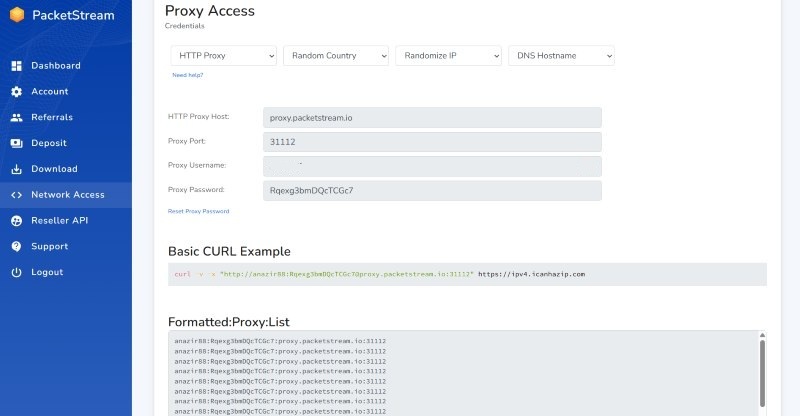
All features are neatly arranged on the left menu, and the main dashboard lies on the right side. With a white background and a few contrasting colors, PacketStream’s interface feels visually appealing and easy to navigate. The average person won’t have any issues understanding this interface: this can’t be said for some proxy providers.
There’s a drawback, though. PacketStream doesn’t offer a browser extension to manage proxies. You need the desktop interface to manage and deploy new proxies, unlike other proxies with browser extensions for seamless proxy management. An extension lets you switch proxies at the click of a single button, but PacketStream doesn’t provide this benefit.
PacketStream: Customer Support
An area where PacketStream lags behind its competitors is customer support. It offers direct support only via email, with no live chat or telephone option. You can send a support email and expect a response within 48 hours, but there’s no option to hold a real-time conversation with support staff.
Also, PacketStream doesn’t provide as many self-help support resources as most competitors. There’s a FAQ section and user guides on the website, but they aren’t as detailed as what we’ve seen in other proxy providers.
PacketStream: The Competition
PacketStream has many competitors, the most notable being Bright Data, Oxylabs, and Decodo (formerly Smartproxy).
Bright Data offers residential, ISP, and datacenter proxies. It also offers advanced web scraping APIs as pre-built datasets. In contrast, PacketStream offers none of these except residential IPs. If you need PacketStream’s proxies for automated data scraping, you’ll need an external platform for the APIs. However, at $1 per GB, PacketStream’s residential proxy service is much more affordable than Bright Data’s, which costs around $8.4 per GB.
Oxylabs provides residential, ISP, and datacenter proxies, with a massive pool of over 100 million IP addresses. It also provides a Web Unblocker and web scraping APIs for enterprises. Oxylabs is undoubtedly the more sophisticated platform. It offers more reliable and speedy proxy IPs, with complete control over its proxy network, unlike peer-to-peer PacketStream. However, Oxylabs’ residential IPs cost $8 per GB, compared to PacketStream’s $1.
Webshare offers residential, ISP, and datacenter proxies, but not web scraping APIs. Its pool of 80 million+ IP addresses across 195 countries is on par with Oxylabs and Bright Data but larger than PacketStream. With pricing as low as $2.8 per GB, Webshare is one of the most affordable proxy providers for enterprises. Yet, PacketStream’s $1 per GB beats it in pricing.
In summary, PacketStream lags slightly behind most competitors in certain advanced features and customer support. However, it outperforms them in ease of use and affordability, helped by the lower costs of running a P2P network and the opportunity to earn money through offering your bandwidth for other users.
PacketStream: Final words
PacketStream is among the most affordable residential IP providers in terms of price per GB, although the minimum purchase is worth $50. This makes it ideal for individual users or small businesses that require rotating and static proxies for mundane online activities. Having said that, enterprises will probably find it lacking for any large-scale data scraping needs. Besides, it lacks the more reliable datacenter and ISP proxies and has limited customer support.







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·