Intel is looking to the future, aiming to make PCs more modular and easier to repair in a move to reduce e-waste. According to the company’s Community post, it is proposing to separate the all-in-one motherboard designs used in laptops into three pieces. It’s also suggesting that mini-PCs, which are traditionally highly integrated and often difficult or impossible to repair or upgrade, be separated into different modules. This move will make these systems far easier to service and would also hopefully reduce the massive amount of e-waste generated each year.
Aside from reparability and upgradability, Intel also claims that its scalable designs for laptops will help reduce the engineering efforts made by their partners.
Essentially, the three modules are the motherboard, and two IO modules. The two IO modules, which are connected to the main motherboard via a flexible printed circuit, and can be reused across various laptop sizes (from 14-inch to 16-inch), models, and designs—from fanless 10W thin-and-light systems to mainstream 20W laptops with a single-fan design and 30W premium laptops that feature dual-fan cooling.

These IO modules can be used across generations, meaning OEMs do not have to completely redesign laptops whenever a new processor or GPU is released. It also leaves the potential for manufacturers to be able to upgrade laptops, including their processor, memory, storage, and wireless modules. Intel also claims that they can be applied to both commercial and consumer designs.
Desktop PCs are already inherently modular, with users able to upgrade their CPU, GPU, memory, storage, and nearly every other module on their computer at home. However, that is not the case for mini-PCs, and Intel wants to change that. The company is proposing breaking down mini-PC modules into three: a CPU module, a GPU module, and a Platform Controller Hub (PCH) module.
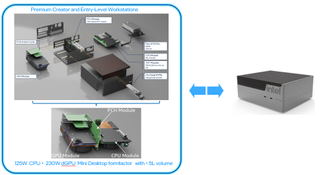
The PCH module would connect the CPU, GPU, and other PCIe add-in cards, allowing for usability just like a typical tower CPU. Intel’s example also showed a 600-watt FlexATX PSU and two hot-swappable NVMe SSDs. Users could then replace these modules at will, making it easier to repair and upgrade them, instead of just replacing the entire system whenever one wants to make a change.
If the majority of PC and laptop manufacturers adopt this technology, this would make repairing and upgrading these devices much easier. This could reduce the amount of e-waste generated each year.
Another example of this approach is Framework. who is already implementing this to some extent. Framework has had some success. For example, we've converted an Intel 13th-gen Framework laptop into an AMD system, and we also reviewed the Framework Laptop 16, which could be user upgraded with a modular discrete GPU.

 2 days ago
4
2 days ago
4








 English (US) ·
English (US) ·