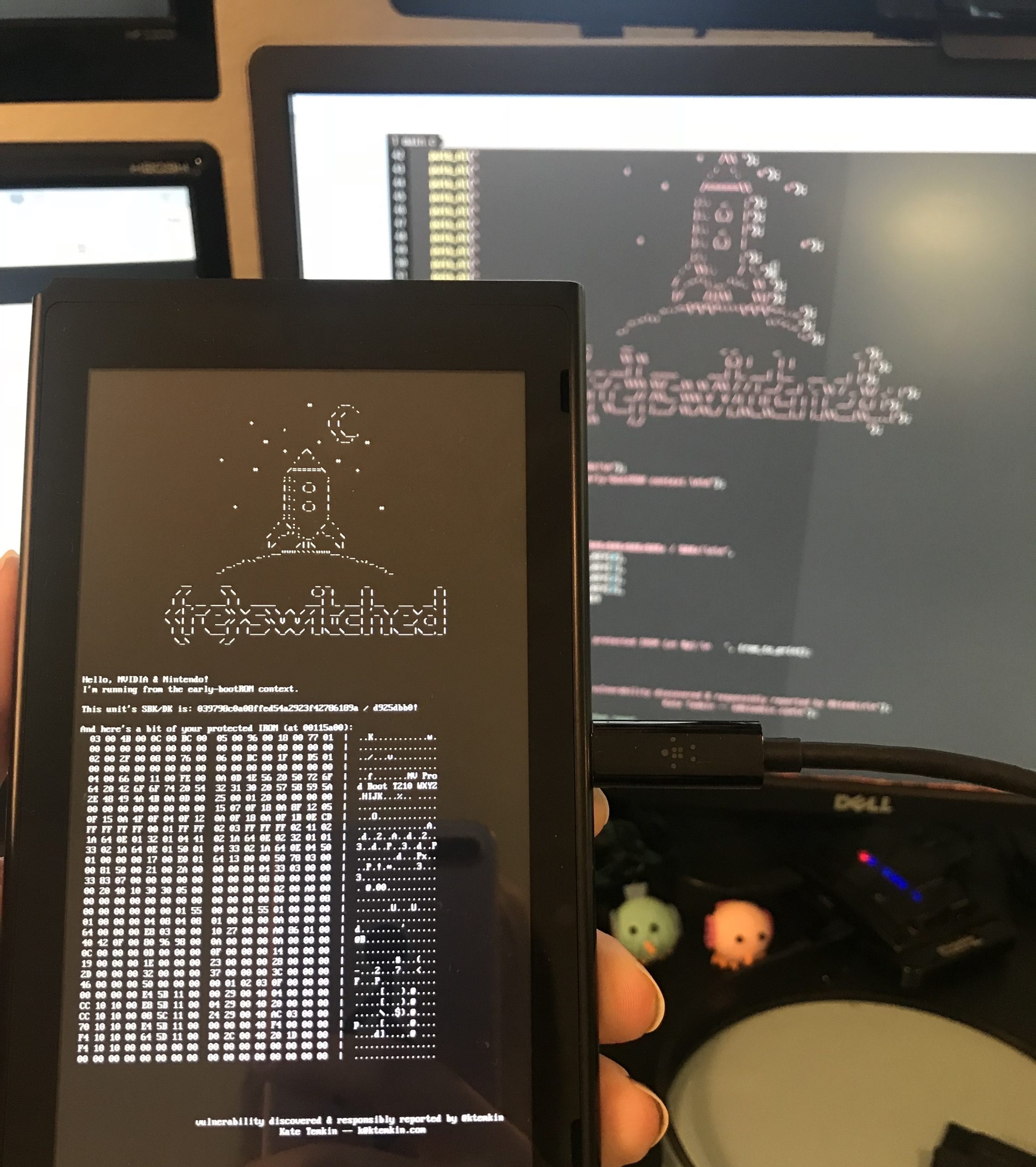
Consoles like these may get banned from Nintendo's online services, but they tend to still work offline. Credit: Kate Temkin / ReSwitched
"Unfortunately, 'bricking' personal devices to limit users’ rights and control their behavior is nothing new," Electronic Frontier Foundation attorney Victoria Noble told Ars Technica. "It would likely take selective enforcement to rise to a problematic level [in court]," attorney Richard Hoeg said.
Last year, a collection of 17 consumer groups urged the Federal Trade Commission to take a look at the way companies use the so-called practice of "software tethering" to control a device's hardware features after purchase. Thus far, though, the federal consumer watchdog has shown little interest in enforcing complaints against companies that do so.
"Companies should not use EULAs to strip people of rights that we normally associate with ownership, like the right to tinker with or modify their own personal devices," Noble told Ars. "[Console] owners deserve the right to make otherwise legal modifications to their own devices without fear that a company will punish them by remotely bricking their [systems]."
The court of public opinion
In the end, these kinds of draconian bricking clauses may be doing their job even if the console makers involved don't invoke them. "In practice, I expect this kind of thing is more about scaring people away from jailbreaking and modifying their systems and that Nintendo is unlikely to go about bricking large volumes of devices, even if they technically have the right to," Loiterman said.
"Just because they put a remedy in the EULA doesn’t mean they will certainly use it either," attorney Mark Methenitis said. "My suspicion is this is to go after the people who eventually succeeded in jailbreaking the original Switch and try to prevent that for the Switch 2."
The threat of public backlash could also hold the console makers back from limiting the offline functionality of any hacked consoles. After citing public scrutiny that companies like Tesla, Keurig, and John Deere faced for limiting hardware via software updates, Methenitis said that he "would imagine Nintendo would suffer similar bad publicity if they push things too far."
That said, legal capacities can sometimes tend to invite their own use. "If the ability is there, someone will want to 'see how it goes.'" Hoeg said.








 English (US) ·
English (US) ·