All the news that's fit to lift
No thunder down under.
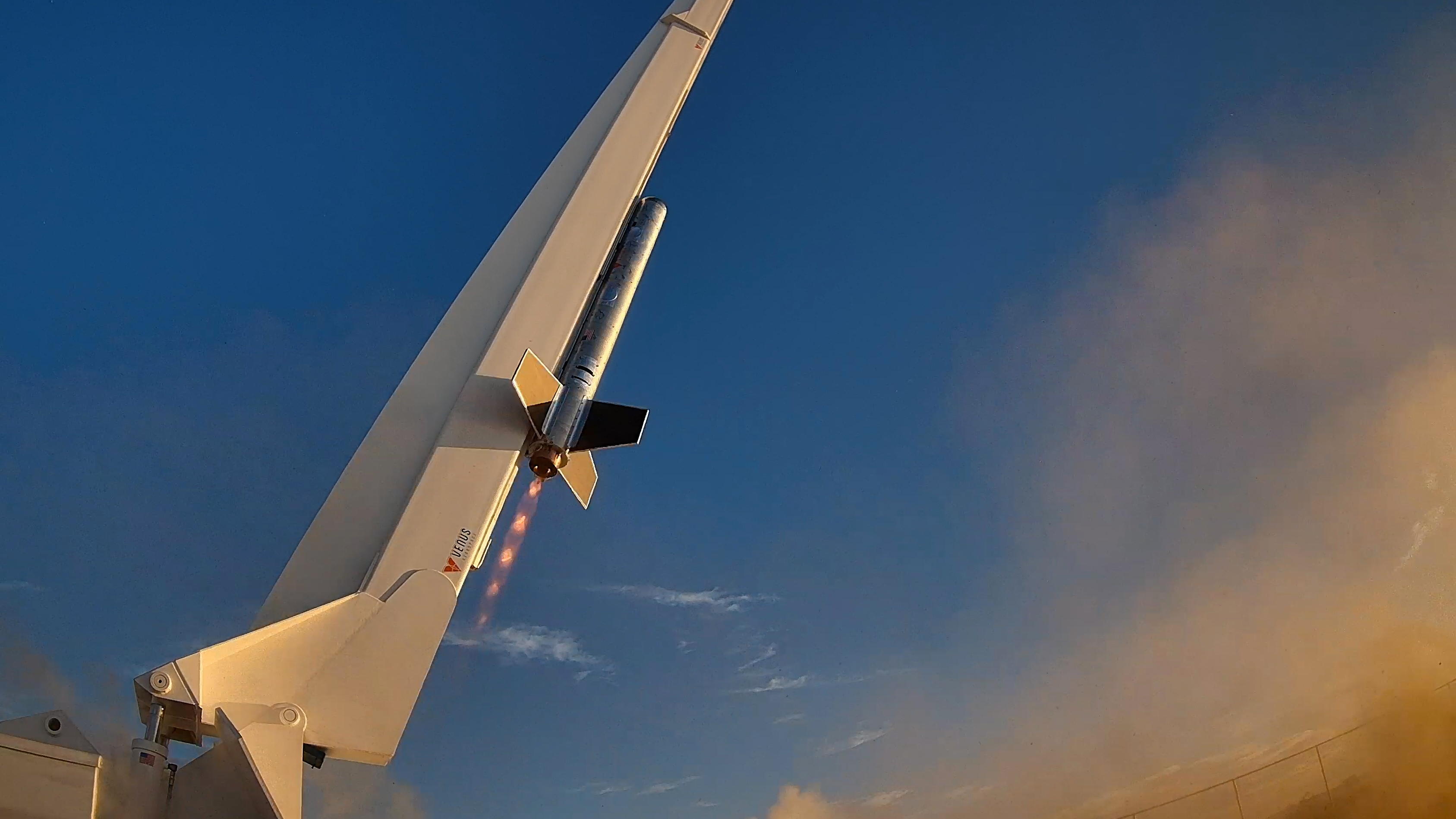
Venus Aerospace tests its rotating detonation rocket engine in flight for the first time this week. Credit: Venus Aerospace
Welcome to Edition 7.44 of the Rocket Report! We had some interesting news on Thursday afternoon from Down Under. As Gilmour Space was preparing for the second launch attempt of its Eris vehicle, as part of the pre-launch preparations, something triggered the payload fairing to deploy. We would love to see some video of that. Please.
As always, we welcome reader submissions, and if you don't want to miss an issue, please subscribe using the box below (the form will not appear on AMP-enabled versions of the site). Each report will include information on small-, medium-, and heavy-lift rockets, as well as a quick look ahead at the next three launches on the calendar.

Rotating detonation rocket engine takes flight. On Wednesday, US-based propulsion company Venus Aerospace completed a short flight test of its rotating detonation rocket engine at Spaceport America in New Mexico, Ars reports. It is believed to be the first US-based flight test of an idea that has been discussed academically for decades. The concept has previously been tested in a handful of other countries, but never with a high-thrust engine.
Hypersonics on the horizon... The company has only released limited information about the test. The small rocket, powered by the company's 2,000-pound-thrust engine, launched from a rail in New Mexico. The vehicle flew for about half a minute and, as planned, did not break the sound barrier. Governments around the world have been interested in rotating detonation engine technology for a long time because it has the potential to significantly increase fuel efficiency in a variety of applications, from Navy carriers to rocket engines. In the near term, Venus' engine could be used for hypersonic missions.
Gilmour Space has a payload fairing mishap. Gilmour Space, a venture-backed startup based in Australia, said this week it was ready to launch a small rocket from its privately owned spaceport on a remote stretch of the country's northeastern coastline, Ars reports. Gilmour's three-stage rocket, named Eris, was prepped for a launch as early as Wednesday, but a ground systems issue delayed an attempt until Thursday US time. And then on Thursday, something odd happened: "Last night, during final checks, an unexpected issue triggered the rocket’s payload fairing," the company said Thursday afternoon, US time.
Always more problems to solve... Gilmour, based in Gold Coast, Australia, was founded in 2012 by two brothers, Adam and James Gilmour, who came to the space industry after careers in banking and marketing. Today, Gilmour employs more than 200 people, mostly engineers and technicians. The debut launch of Gilmour's Eris rocket is purely a test flight. Gilmour has tested the rocket's engines and rehearsed the countdown last year, loading propellant and getting within 10 seconds of launch. But Gilmour cautioned in a post on LinkedIn early Wednesday that "test launches are complex." And it confirmed that on Thursday. Now the company will need to source a replacement fairing, which will probably take a while.
The easiest way to keep up with Eric Berger's and Stephen Clark's reporting on all things space is to sign up for our newsletter. We'll collect their stories and deliver them straight to your inbox.
Is an orbital launch from Argentina imminent? We don't know much about the Argentinian launch company TLON Space, which is developing a (very) small-lift orbital rocket called Aventura 1. According to the company's website, this launch vehicle will be capable of lofting 25 kg to low-Earth orbit. Some sort of flight test took place two years ago, but the video cuts off after a minute, suggesting that the end of the flight was less than nominal.
Maybe, maybe not... Now, a publication called Urgente24 reports that an orbital launch attempt is underway. It is not clear exactly what this means, and details about what is actually happening at the Malacara Spaceport in Argentina are unclear. I could find no other outlets reporting on an imminent launch attempt. So my guess is that nothing will happen soon, but it is something we'll keep an eye on regardless. (Submitted by fedeng.)
Poland launches suborbital rocket. Poland has successfully launched a single-stage rocket demonstrator at the Central Air Force Training Ground in Ustka, European Spaceflight reports. The flight was part of a project to develop a three-stage solid-fuel rocket for research payloads. In 2020, the Polish government selected Wojskowe Zakłady Lotnicze No. 1 to lead a consortium developing a three-stage suborbital launch system.
Military uses eyed... The Trójstopniowa Rakieta Suborbitalna (TRS) project involves the Military Institute of Armament Technology and Zakład Produkcji Specjalnej Gamrat and is co-financed by the National Center for Research and Development. The goal of the TRS project is to develop a three-stage rocket capable of carrying a 40-kilogram payload to an altitude exceeding 100 kilometres. While the rocket will initially be used to carry research payloads into space, Poland’s Military Institute of Armament Technology has stated that the technology could also be used for the development of anti-aircraft and tactical missiles.
Latitude signs MoU to launch microsats. On Wednesday, the French launch firm Latitude announced the signing of a memorandum of understanding for the launch of a microsatellite constellation dedicated to storing and processing data directly in orbit. In an emailed news release, Latitude said the "strategic partnership" represents a major step forward in strengthening collaborations between UAE and French space companies.
That's a lot of launches... Madari Space is developing a constellation of microsatellites (50 to 100 kg), designed as true orbital data centers. Their mission is to store and process data generated on Earth or by other satellites. Latitude plans its first commercial launch with its small-lift Zephyr rocket as early as 2026, with the ambition of reaching a rate of 50 launches per year from 2030. An MoU represents an agreement but not a firm launch contract.

China begins launching AI constellation. China launched 12 satellites early Wednesday for an on-orbit computing project led by startup ADA Space and Zhejiang Lab, Space News reports. A Long March 2D rocket lifted off at 12:12 am Eastern on Wednesday from Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in northwest China. Commercial company ADA Space released further details, stating that the 12 satellites form the “Three-Body Computing Constellation,” which will directly process data in space rather than on the ground, reducing reliance on ground-based computing infrastructure.
Putting the intelligence in space... ADA Space claims the 12 satellites represent the world’s first dedicated orbital computing constellation. This marks a shift from satellites focused solely on sensing or communication to ones that also serve as data processors and AI platforms. The constellation is part of a wider “Star-Compute Program,” a collaboration between ADA Space and Zhejiang Lab, which aims to build a huge on-orbit network of 2,800 satellites. (Submitted by EllPeaTea.)
SpaceX pushes booster reuse record further. SpaceX succeeded with launching 28 more Starlink satellites from Florida early Tuesday morning following an overnight scrub the previous night. The Falcon 9 booster, 1067, made a record-breaking 28th flight, Spaceflight Now reports.
Booster landings have truly become routine... A little more than eight minutes after liftoff, SpaceX landed B1067 on its drone ship, Just Read the Instructions, which was positioned in the Atlantic Ocean to the east of the Bahamas. This marked the 120th successful landing for this drone ship and the 446th booster landing to date for SpaceX. (Submitted by EllPeaTea.)

What happens if Congress actually cancels the SLS rocket? The White House Office of Management and Budget dropped its "skinny" budget proposal for the federal government earlier this month, and the headline news for the US space program was the cancellation of three major programs: the Space Launch System rocket, the Orion spacecraft, and the Lunar Gateway. In a report, Ars answers the question of what happens to Artemis and NASA's deep space exploration plans if that happens. The most likely answer is that NASA turns to an old but successful playbook: COTS.
A market price for the Moon... This stands for Commercial Orbital Transportation System and was created by NASA two decades ago to develop cargo transport systems (eventually, this became SpaceX's Dragon and Northrop's Cygnus spacecraft) for the International Space Station. Since then, NASA has adopted this same model for crew services as well as other commercial programs. Under the COTS model, NASA provides funding and guidance to private companies to develop their own spacecraft, rockets, and services and then buys those at a "market" rate. Sources indicate that NASA would go to industry and seek an "end-to-end" solution for lunar missions—that is, an integrated plan to launch astronauts from Earth, land them on the Moon, and return them to Earth.
Starship nearing its next test flight. SpaceX fired six Raptor engines on the company's next Starship rocket Monday, clearing a major hurdle on the path to launch later this month on a high-stakes test flight to get the private rocket program back on track. SpaceX hasn't officially announced a target launch date, but sources indicate a launch could take place toward the end of next week, prior to Memorial Day weekend, Ars reports. The launch window would open at 6:30 pm local time (7:30 pm EDT; 23:30 UTC).
Getting back on track... If everything goes according to plan, Starship is expected to soar into space and fly halfway around the world, targeting a reentry and controlled splashdown into the Indian Ocean. While reusing the first stage is a noteworthy milestone, the next flight is important for another reason. SpaceX's last two Starship test flights ended prematurely when the rocket's upper stage lost power and spun out of control, dropping debris into the sea near the Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands.
Next three launches
May 16: Falcon 9 | Starlink 15-5 | Vandenberg Space Force Base, California | 13:43 UTC
May 17: Electron | The Sea God Sees | Māhia Peninsula, New Zealand | 08:15 UTC
May 18: PSLV-XL | RISAT-1B | Satish Dhawan Space Centre, India | 00:29 UTC

Eric Berger is the senior space editor at Ars Technica, covering everything from astronomy to private space to NASA policy, and author of two books: Liftoff, about the rise of SpaceX; and Reentry, on the development of the Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon. A certified meteorologist, Eric lives in Houston.









 English (US) ·
English (US) ·