A new Linux kernel patch brings hardware enablement for Intel's Bartlett Lake-S family of processors. In the same patch, an Intel engineer has seemingly confirmed the existence of a P-core-only counterpart to Bartlett Lake, via Phoronix. This update enables the kernel to properly identify these processors at boot, assigning them a CPUID for recognition in software. Likewise, these CPUIDs also allow the compiler to execute hardware-specific code path optimizations using the Intel CPU dispatcher mechanism.
At CES, Intel formally introduced the Bartlett Lake-S platform, which includes three CPUs configured with hybrid cores intended for NEX (Network and Edge) applications. Since last year, rumors have alleged the existence of a performance-core-only analog, wielding up to 12P cores and 24 threads. Bartlett Lake targets the LGA 1700 platform, so these CPUs should be drop-in replacements for existing 600-series and 700-series motherboards, after updating the BIOS, of course.
The Intel engineer added an identification entry for Bartlett Lake CPUs in the Linux kernel, assigning them to CPU Family 6, Model 215 (0xD7). These codenames allow the software to determine the processor family and whether it supports certain hardware instructions or not. The engineer additionally noted, "Bartlett Lake has a P-core only product with Raptor Cove", which effectively corroborates all previous leaks.
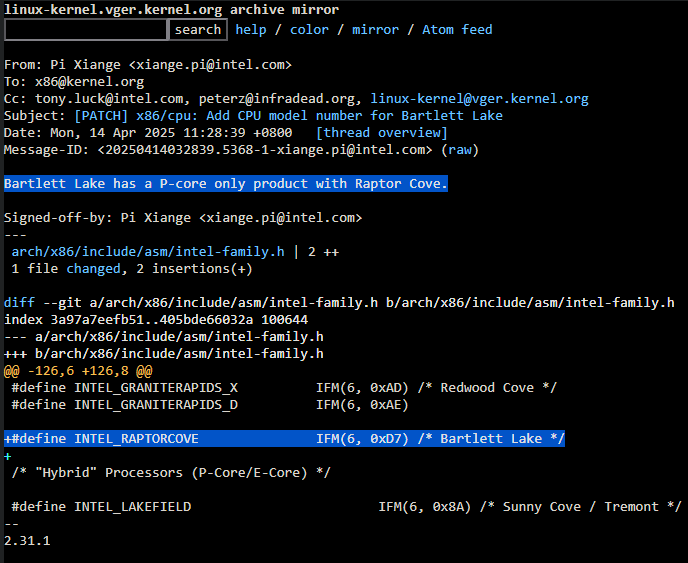
The Raptor Cove micro-architecture is an enhanced version of Golden Cove and powers the performance cores of Intel's 13th and 14th Generation processors. Pertinently, Bartlett Lake-S (P-core only) is reported to utilize a new die, as all Raptor Lake silicon is limited to just eight performance cores. The same leaker suggests these processors will debut in 125W/65W/45W configurations, catering to a wide variety of customers.
The elephant in the room is availability. Existing Bartlett Lake options are limited to embedded packages like COM-HPCs. Monolithic core configurations can clear up scheduling headaches and open a door for Intel to re-enable AVX-512 instruction support, which has been fused off silicon since later Alder Lake batches.
Bartlett Lake could be a double-edged sword; you'd likely see improved gaming performance, but at the cost of efficiency versus Arrow Lake. This might be a compromise gamers are willing to make, though, whether these chips can hold their own against AMD's Ryzen 9000 series remains to be seen. The rumor mill suggests a Q3 25 (July-September) release window for these processors, so we might be in for an announcement at Computex, next month.

 6 months ago
96
6 months ago
96







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·